
Recently, the Companion Animal Biosafety Risk Warning and Control Technology Team of SHVRI CAAS, successfully developed a novel monoclonal-antibody-based sandwich ELISA for the rapid and quantitative detection of Fel d 1, the primary allergen produced by cats. The breakthrough provides an important tool for assessing environmental allergen exposure and preventing pet-related respiratory allergies. The study was recently published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.
Background
Fel d 1 is the most potent cat-derived allergen and a major cause of allergic rhinitis, asthma, and conjunctivitis in humans. Secreted by the salivary and sebaceous glands, the protein easily spreads through hair and dander and can persist in indoor environments, even where no cats are present. A sensitive, economical, and standardized detection method is therefore critical for monitoring public exposure levels.
Research Progress
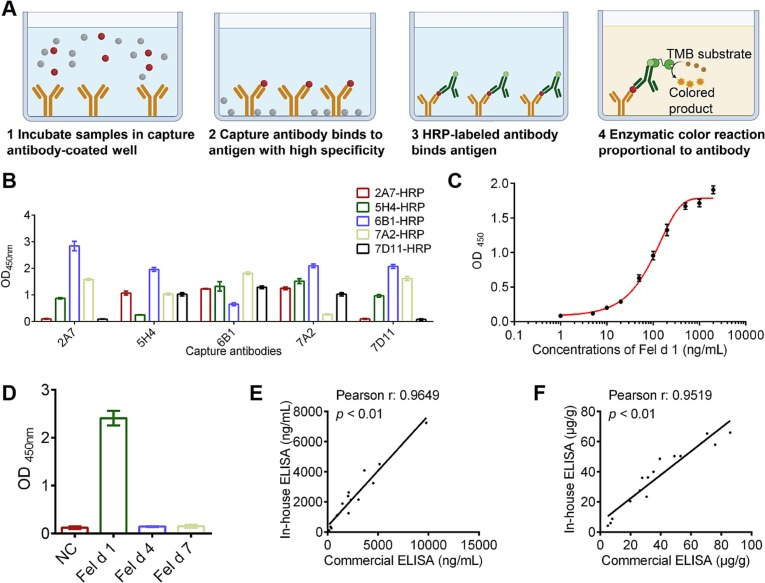
Herein, we report the generation and validation of several high-affinity monoclonal antibodies targeting the Fel d 1 protein, which were subsequently employed in the construction of a double-antibody sandwich ELISA. The newly developed assay achieves a detection limit of 1 ng/mL and a linear range of 10–500 ng/mL, demonstrating excellent specificity without cross-reactivity to other cat-derived allergenic proteins. Tests on real cat saliva and hair samples also showed strong consistency with results from a commercial detection kit (correlation coefficient r > 0.95), confirming the method’s accuracy and reliability.Further epitope analysis revealed that the two monoclonal antibodies recognise distinct α-helical structural regions of the Fel d 1 protein. These findings provide a valuable structural basis for future mechanistic studies and the development of allergen-targeted vaccines.This new ELISA method offers an effective, home-grown tool for quantitative detection of Fel d 1 and supports the establishment of a comprehensive monitoring system for pet allergen exposure.
Development and Validation of a Rapid Detection Method for Fel d 1 Allergen Protein
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant 2024M753586) and the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant 2023YFD1800705). The study was co-first authored by PhD candidate Zhuangli Bi and master’s student Linying Cai from SHVRI. Professor Guangqing Liu and postdoctoral fellow Yinqi Zhu served as corresponding authors.
Link to Original Article
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.147129

