
Recently, the Schistosomiasis Research Team of SHVRI CAAS, discovered that microRNAs secreted by Schistosoma japonicum play a key role in regulating liver fibrosis in the host. The related research findings have been published in Acta Tropica.
Background and research progress
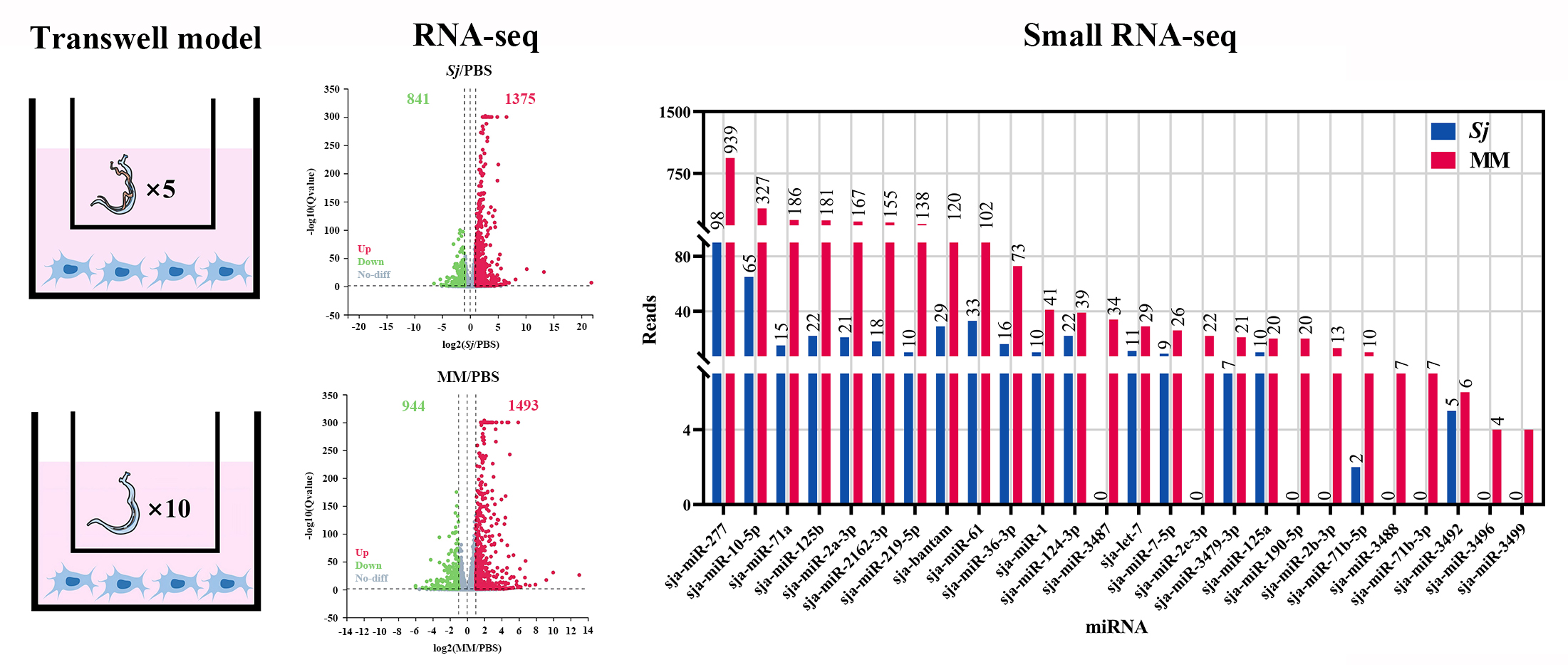
Liver fibrosis is one of the major complications caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection. While previous studies mainly focused on immune responses induced by schistosome eggs, the direct role of schistosome worms in pathological changes of the host liver has not been fully elucidated. Through microRNA sequencing, this study revealed that microRNAs secreted by schistosome worms significantly contribute to the activation of hepatic stellate cells, a central event in liver fibrosis. The results showed that both paired worms and single male schistosomes can activate hepatic stellate cells by secreting microRNAs, thereby inducing liver fibrosis.
“Molecular Weapon” from Schistosomes to Manipulate Host Liver Fibrosis
Zhong Haoran, Assistant Researcher from SHVRI, is the first author of the paper, and Researcher Jin Yamei is the corresponding author. This research was supported by the “Sailing Program” of the Shanghai Rising-Star Program and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of CAAS.
Original article link
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0001706X25002189

